

(iii) The minimum of the CDF is when x 1 : F X(1 ) 0. (ii) The maximum of the CDF is when x 1: F X(+1) 1. The cumulative distribution function for any random variable X, denoted by F( x), is the probability that X assumes a value less than or equal to x:į ( x ) = Pr ( X ≤ x ) Let X be a random variable (either continuous or discrete), then the CDF of X has the following properties: (i) The CDF is a non-decreasing. To make this definition more precise, we recall the definition from Section 1.4 of a cumulative distribution function (CDF) that was given for any random variable. I understand that any C.D.F may be represented in the form F (x) p1Fd (x) + p2Fc (x), where Fd (x) represents discrete c.d.f, Fc (x) represents continuous c.d.f and p1+ p21. Analyzing and processing random signals and designing filters that adapt to. For example, we can define a continuous random variable that can take on any value in the interval. Video created by for the course 'Digital Signal Processing 2: Filtering'.
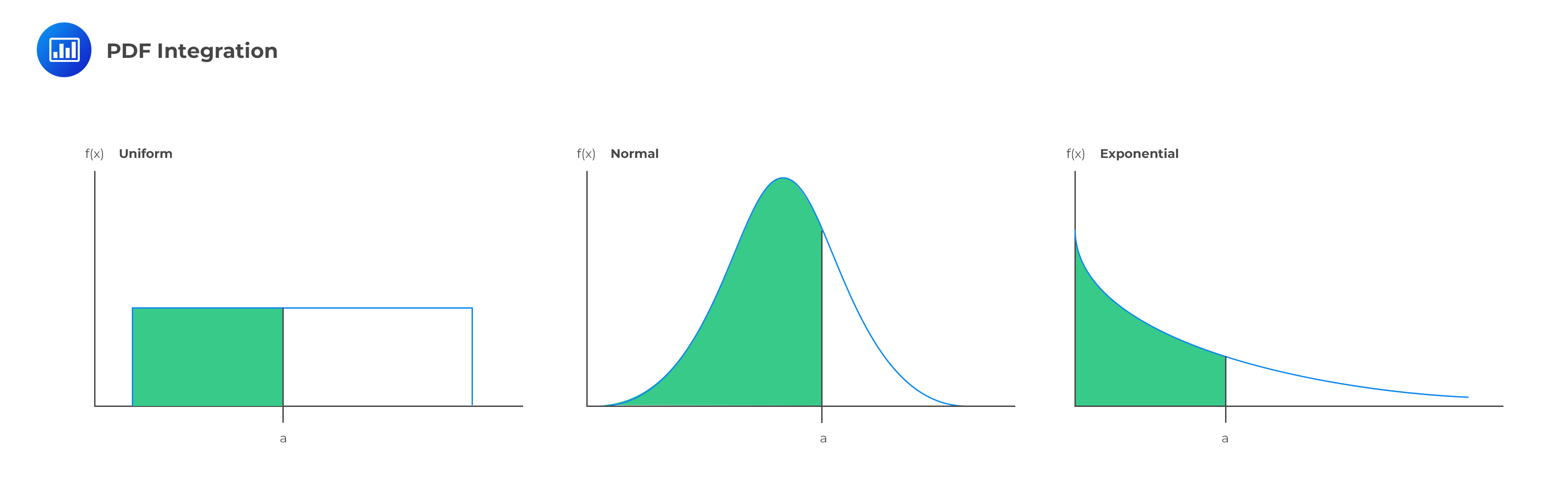
We previously defined a continuous random variable to be one where the values the random variable can assume are given by a continuum of values. If for example X is the height of a randomly selected person in British Columbia, or X is tomorrow's low temperature at Vancouver International Airport, then X is a continuously varying quantity. In this chapter, we properly treat continuous random variables.

In the previous chapter, we defined random variables in general, but focused only on discrete random variables.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
